
MobX
Simple, scalable state management.
README

MobX
_Simple, scalable state management._
Documentation
Documentation can be found at mobx.js.org.
Sponsors
MobX is made possible by the generosity of the sponsors below, and many other individual backers. Sponsoring directly impacts the longevity of this project.




















Introduction
_Anything that can be derived from the application state, should be. Automatically._
MobX is a battle-tested library that makes state management simple and scalable by transparently applying functional reactive programming.
The philosophy behind MobX is simple:
😙
Straightforward
Write minimalistic, boilerplate-free code that captures your intent.
Trying to update a record field? Simply use a normal JavaScript assignment —
the reactivity system will detect all your changes and propagate them out to where they are being used.
No special tools are required when updating data in an asynchronous process.
🚅
Effortless optimal rendering
All changes to and uses of your data are tracked at runtime, building a dependency tree that captures all relations between state and output.
This guarantees that computations that depend on your state, like React components, run only when strictly needed.
There is no need to manually optimize components with error-prone and sub-optimal techniques like memoization and selectors.
🤹🏻♂️
Architectural freedom
MobX is unopinionated and allows you to manage your application state outside of any UI framework.
This makes your code decoupled, portable, and above all, easily testable.
A quick example
So what does code that uses MobX look like?
- ``` js
- import React from "react"
- import ReactDOM from "react-dom"
- import { makeAutoObservable } from "mobx"
- import { observer } from "mobx-react"
- // Model the application state.
- class Timer {
- secondsPassed = 0
- constructor() {
- makeAutoObservable(this)
- }
- increase() {
- this.secondsPassed += 1
- }
- reset() {
- this.secondsPassed = 0
- }
- }
- const myTimer = new Timer()
- // Build a "user interface" that uses the observable state.
- const TimerView = observer(({ timer }) => (
- <button onClick={() => timer.reset()}>Seconds passed: {timer.secondsPassed}</button>
- ))
- ReactDOM.render(<TimerView timer={myTimer} />, document.body)
- // Update the 'Seconds passed: X' text every second.
- setInterval(() => {
- myTimer.increase()
- }, 1000)
- ```
The observer wrapper around the TimerView React component will automatically detect that rendering
depends on the timer.secondsPassed observable, even though this relationship is not explicitly defined. The reactivity system will take care of re-rendering the component when _precisely that_ field is updated in the future.
Every event (onClick / setInterval) invokes an _action_ (myTimer.increase / myTimer.reset) that updates _observable state_ (myTimer.secondsPassed).
Changes in the observable state are propagated precisely to all _computations_ and _side effects_ (TimerView) that depend on the changes being made.
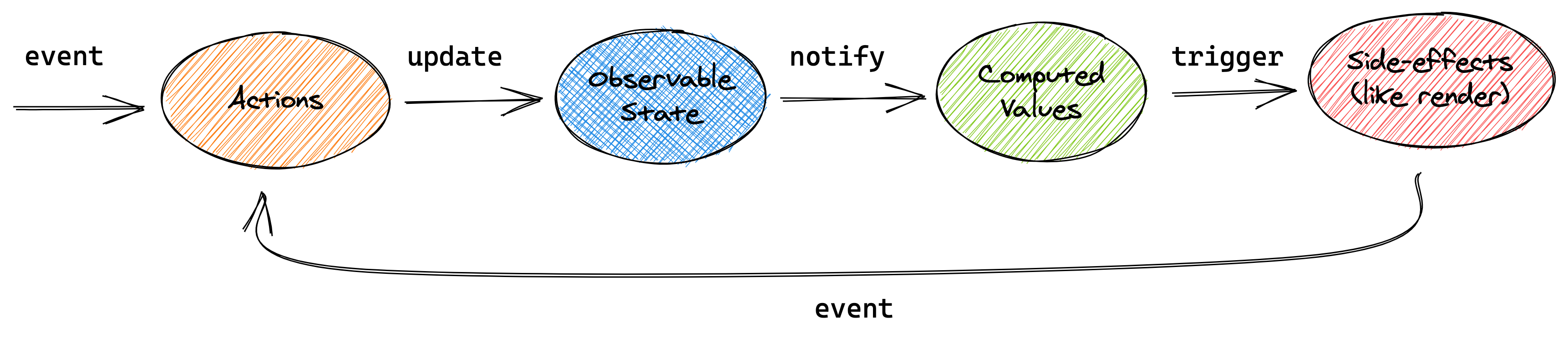
This conceptual picture can be applied to the above example, or any other application using MobX.
Getting started
To learn about the core concepts of MobX using a larger example, check out The gist of MobX page, or take the 10 minute interactive introduction to MobX and React.
The philosophy and benefits of the mental model provided by MobX are also described in great detail in the blog posts UI as an afterthought and How to decouple state and UI (a.k.a. you don’t need componentWillMount).
Further resources
- The MobX cheat sheet (£5) is both useful and sponsors the project
- The MobX awesome list – a long list of MobX resources and example projects
The MobX book

The MobX Quick Start Guide ($24.99) by Pavan Podila and Michel Weststrate is available as an ebook, paperback, and on the O'Reilly platform (see preview).
Videos
- Introduction to MobX & React in 2020 by Leigh Halliday, _17 min_.
- ReactNext 2016: Real World MobX by Michel Weststrate, _40 min_, slides.
- CityJS 2020: MobX, from mutable to immutable, to observable data by Michel Weststrate, _30 min_.
- OpenSourceNorth: Practical React with MobX (ES5) by Matt Ruby, _42 min_.
- HolyJS 2019: MobX and the unique symbiosis of predictability and speed by Michel Weststrate, _59 min_.
- React Amsterdam 2016: State Management Is Easy by Michel Weststrate, _20 min_, slides.
- {🚀} React Live 2019: Reinventing MobX by Max Gallo, _27 min_.
Credits
MobX is inspired by reactive programming principles, which are for example used in spreadsheets. It is inspired by model–view–viewmodel frameworks like MeteorJS's Tracker, Knockout and Vue.js, but MobX brings _transparent functional reactive programming_ (TFRP, a concept which is further explained in the MobX book) to the next level and provides a standalone implementation. It implements TFRP in a glitch-free, synchronous, predictable and efficient manner.
A ton of credit goes to Mendix, for providing the flexibility and support to maintain MobX and the chance to prove the philosophy of MobX in a real, complex, performance critical applications.
 探客时代
探客时代



